As generative AI tools like ChatGPT continue to advance, they are revolutionizing how Talent Development (TD) professionals create learning experiences. AI in TD is often categorized into three levels: Level 1, focused on enhancing efficiency in existing tasks; Level 2, where learners directly interact with AI for personalized support; and Level 3, where AI seamlessly integrates into workflows.
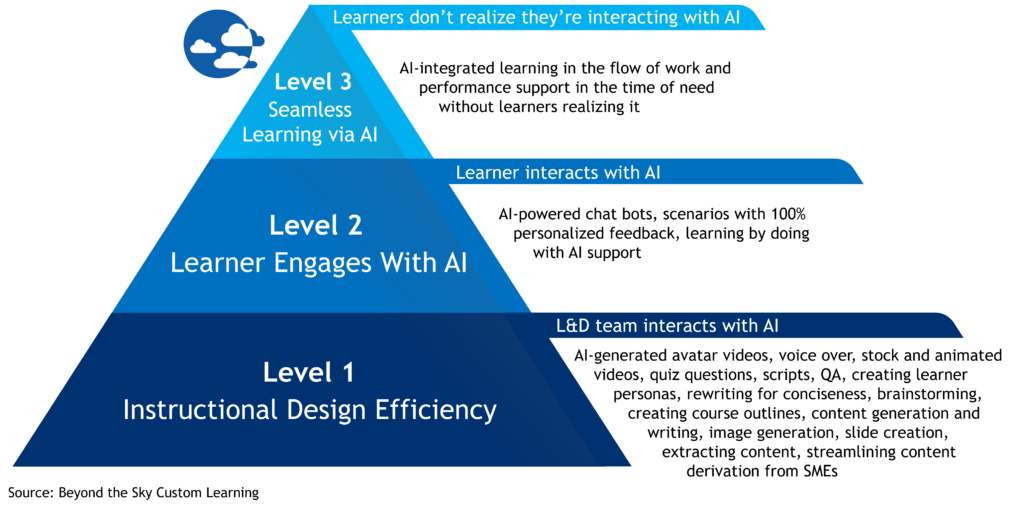
At the “Level 2” stage of AI use in TD, learners interact directly with AI systems, gaining a personalized, responsive experience that enhances their learning outcomes. This level of interaction shifts AI’s role from efficiency to learning by doing, moving beyond content creation or analysis to offer coaching, feedback, performance assessment, and real-time support. Below are some impactful ways Level 2 AI can support TD initiatives.
1. AI as a Digital Coach for Personalized Feedback
Generative AI can act as a digital coach, providing instant, personalized feedback on learners’ responses. Acting as a supportive guide, an AI-powered digital coach can evaluate how learners approach tasks and identify specific areas for improvement.
Imagine a learner practicing a presentation: the AI speaker coach can assess pacing, pronunciation, body language, and clarity, then offer targeted feedback to refine their communication skills. This instant coaching enables learners to address weaknesses, refine their approach, and build confidence. Many organizations have this free feature already enabled in their existing PowerPoint subscription but are unaware of it.
In another example, consider a big meeting whereby the AI coach could guide learners through a series of thoughtful questions to help them clarify their goals, anticipate potential challenges, and unlock insights—just as an effective human coach would. This reflective questioning helps learners find answers within themselves, strengthening their readiness and self-assurance. Try this AI coach example yourself (I’ll re-add the link to try shortly). While this doesn’t replace a human coach, it provides support on demand and is particularly useful for remote learners, those with tight schedules, or when human coaching isn’t possible.
2. Effective AI Use Case as FAQ for Performance Support
One of the most immediate and accessible effective AI use cases at Level 2 is creating a responsive FAQ system that provides accurate, customized answers to learner questions. Instead of relying on static documents or navigating through multiple files, learners can simply ask the AI questions and receive precise, tailored answers. This enhanced frequently asked question (FAQ) function serves as an invaluable tool for performance support, enabling employees to get the information they need in real-time.
For instance, we have our internal Beyond the Sky chatbot for our team. If a team member asks, “What are the steps in our quality assurance process?” the AI can instantly provide a clear outline, including details on file submission and deadlines. By tapping into an internal knowledge repository, this AI functions as an accessible knowledge base, significantly reducing the time learners spend searching for information and enhancing productivity.
3. Onboarding Concierge for New Hires
Another effective AI use case at Level 2 is deploying AI as an onboarding concierge, offering a welcoming experience for new hires by providing essential information on demand. New employees often have numerous questions about company policies, processes, and workflows, and a personalized AI concierge can answer these questions in real-time, helping them acclimate more smoothly.
The AI onboarding assistant could answer questions like, “How do I submit a time-off request?” or “Who should I contact for IT issues?” By guiding new hires through their initial queries and needs, the AI concierge ensures a smoother transition and reduces the pressure on managers and HR personnel, making onboarding more efficient and effective.
4. Practicing Difficult Conversations through Scenarios
Level 2 AI can support employees in practicing challenging conversations in a safe, simulated environment, showcasing an effective AI use case for skill development. Learners can engage in role-play scenarios with the AI, testing out responses to difficult questions or practicing how to handle sensitive issues. For example, an employee could use AI to rehearse a conversation with a client dissatisfied with a service, receiving instant feedback on tone, phrasing, and empathy.
Similarly, AI can guide learners in preparing for uncomfortable conversations, such as providing constructive feedback to a colleague or addressing a performance issue, by offering tips on maintaining a respectful tone and clear message. You can try practicing a difficult conversation yourself with 100% personalized AI feedback (I’ll re-add the link to try shortly).
This application of AI not only helps learners build confidence in handling complex situations but also allows them to develop their soft skills in a controlled setting, without the potential repercussions of real-world errors. By providing feedback on phrasing, tone, and word choice, the AI helps learners refine their approach, making them more effective communicators.
5. Rating Customer Interactions: An Effective AI Use Case for Addressing Gaps
I recently spoke with an organization implementing one of the most effective AI use cases I’ve seen by using AI to provide valuable insights for their call center agents. By analyzing customer interactions and rating agents on key performance indicators like empathy, clarity, and problem-solving skills, the AI enabled the organization to achieve insights that simply weren’t possible if managers or coaches had to listen to every conversation.
This AI-powered evaluation allowed agents to understand how well they were meeting customer needs and offered targeted feedback for improvement on subsequent calls. For instance, the AI could assess an agent’s tone and clarity during a call, highlight areas where empathy could be enhanced, or suggest strategies for managing difficult clients more effectively. The data collected also helped guide the organization in identifying areas where further training might be beneficial, demonstrating AI’s role in optimizing performance in real time.
6. Effective AI Use Case for Self-Quizzing and Knowledge Retention
AI-powered tools like ChatGPT can serve as interactive self-quizzing platforms, enabling learners to independently test and strengthen their knowledge. This effective AI use case allows learners to prompt the AI to generate questions on specific topics, challenging them to recall information, assess their understanding, and focus on areas needing improvement. This personalized quizzing is especially valuable for topics requiring ongoing retention, as learners can engage in repeated practice on demand.
For example, a learner studying certification guidelines could use ChatGPT to quiz themselves on essential policies and requirements, helping them retain critical information. My son recently used generative AI to create essay questions to prepare for an upcoming exam on 1984. Because the book is widely discussed online, ChatGPT was able to generate thought-provoking questions about its themes. He then used the AI to grade his responses and receive feedback on how he could improve. Additionally, he could adjust the complexity of the questions, such as asking for “an essay question at a grade 9 level” versus “an essay question at a first-year university level.” This variation helped him uncover new perspectives and connect themes to modern contexts. When it came time to take the exam, he achieved a high score in a subject he typically finds challenging.
Having learners directly engage with generative AI—not just Talent Development professionals using it for efficiency—enables applied practice and critical thinking. This shows how AI can be a valuable tool for preparing learners across a range of tasks, from general learning to complex assessments.
7. Evaluating Meeting Performance: An Effective AI Use Case for Building Soft Skills
AI’s real-time analysis capabilities can extend to evaluating a learner’s performance in meetings, focusing on essential soft skills like active listening, confidence, and engagement. This effective AI use case enables learners to receive feedback on behaviors such as dominating conversations, demonstrating active listening, or displaying appropriate confidence. This evaluation promotes self-awareness and helps learners understand how they are perceived in team settings.
For instance, if a learner consistently dominates conversations, the AI can provide feedback on balancing input with listening. This evaluation process helps learners refine their interpersonal skills, improving their individual performance and their contributions in collaborative environments.
In our organization, we use firefly.ai and I actively track my tone, whether I’m speaking to much, which words I overuse, and how well run our meetings are. The analytics are helpful after a meeting and to track trends in skill development.
8. Assessing Soft Skills: An Effective AI Use Case
Beyond performance in meetings, Level 2 AI could offer broader assessments of essential soft skills, including teamwork, adaptability, and emotional intelligence. In this effective AI use case, learners engage in AI-driven assessments that provide targeted feedback on specific skills, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. For example, an employee could use AI embedded into an eLearning to assess their adaptability by simulating different workplace challenges and evaluating their responses. Generative AI provides specific feedback and a numerical rating to indicate how the learner fares.
On a smaller scale, I use generative AI to evaluate areas of improvement and I ask for feedback. This cathartic and free Tactful Tone Transformer GPT I created helps me rewrite any emotionally charged message grades me in my response.
Overall, by identifying specific soft skills that require development, learners can take proactive steps to improve, supported by AI-generated feedback tailored to their progress and growth areas.
Conclusion
Level 2 AI applications in Talent Development are transforming traditional learning interactions by offering learners personalized, real-time support that goes beyond static content delivery. Whether serving as a digital coach, performance evaluator, or interactive FAQ, AI has the potential to provide learners with the guidance, feedback, and information they need exactly when they need it. These AI-powered interactions not only enhance learning experiences but also allow learners to refine critical skills, gain valuable insights into their performance, and take control of their professional growth.
These effective AI use cases are particularly important as the business world faces a natural shift towards level 1 use cases as subject matter experts use AI to create content faster. In turn, the modern workforce is trending to rely on AI for speed risks while risking quality. I suggest that we also focus on instructionally sound effective AI use cases where we elevate learning experiences and provide meaningful, “learning by doing” interactions. Embracing Level 2 AI applications allows TD teams to balance efficiency with quality, building adaptive, personalized learning environments that drive genuine growth in an evolving workplace.


Recent Comments